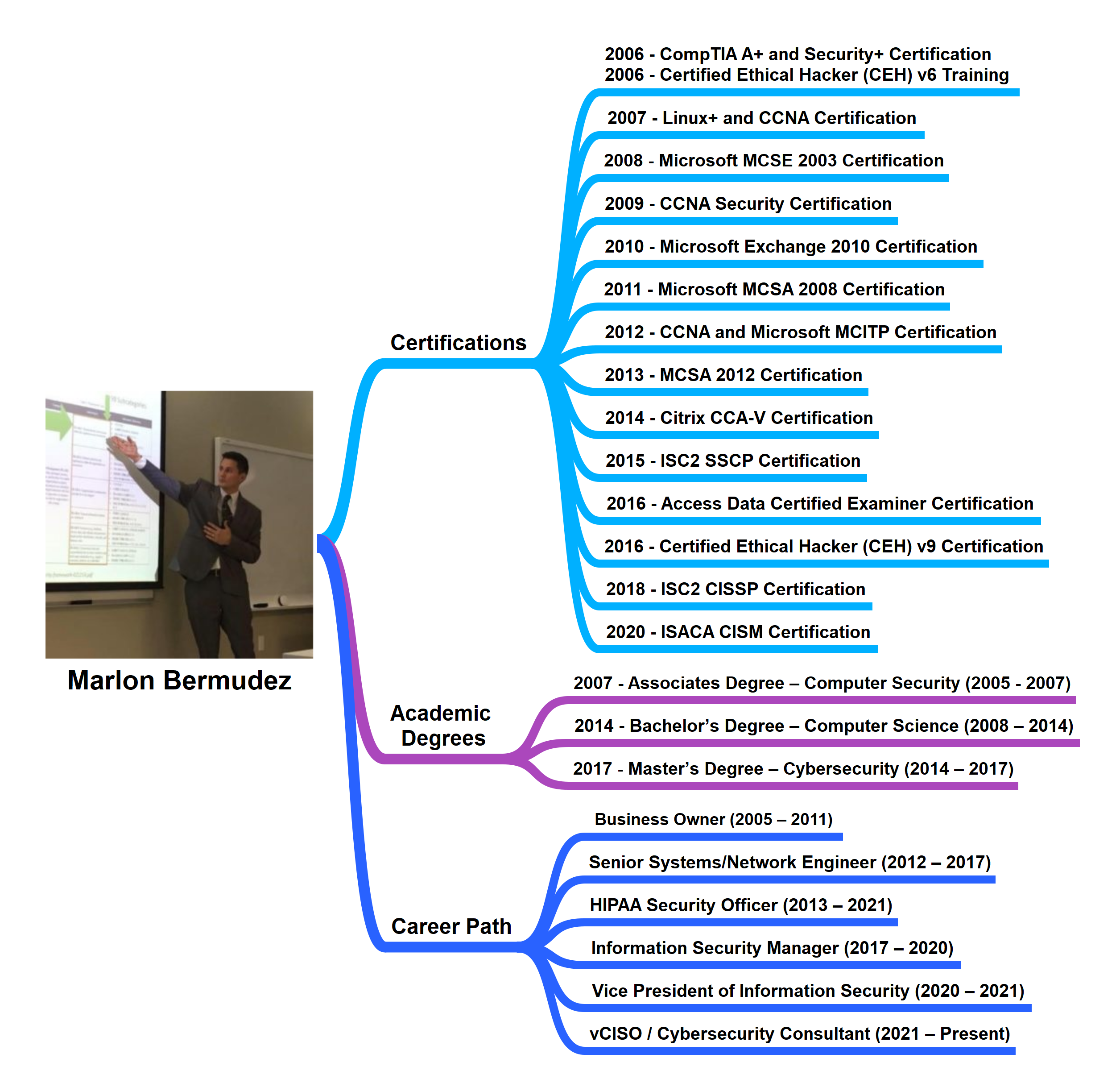
Marlon Bermudez is a seasoned, experienced, and certified Information Security Professional with over 15 years of experience.
At the age of nineteen, he established his own IT company through which he helped small business owners and end-users with their technology needs. As a consultant, he proposed and implemented technology to support business needs, information security, and growth.
While he enjoyed having a successful business, five years later, he decided to join a Managed Service Provider to be able to help small businesses on a larger scale. He has been working full time to help small and midsize businesses since 2012 as a Senior Network/Systems Engineer; since 2013 as a HIPAA Security Officer; 2017-2020 as an Information Security Manager, 2020-2021 as Vice President of Information Security at U.S. Computer Connection LLC.
In 2021 he published his book Cybersecurity for Small and Midsize Businesses, and in 2021 became a virtual Chief Information Security Officer (vCISO) / Cybersecurity Consultant and Founder of Marber Security LLC.
His experience expands well beyond the technical role; into leadership, management, operations, and cyber-security.
Bermudez’s passion for cybersecurity and his commitment to helping small and midsize businesses have led him to write this book to help organizations protect themselves. The following is a summary of his academic and professional accomplishments.
A few words from the Founder
A single data or security breach can have a devastating and permanent impact that can put an organization out of business after just a single incident.
Laws and regulations apply to all organizations, and most cybersecurity requirements are the same for organizations regardless of their size. As I enthusiastically obtained my IT and cybersecurity certifications, completed my Master of Science in Cybersecurity, and supported the IT and cybersecurity needs of small and midsize businesses, it became apparent that small and midsize businesses are at a disadvantage. Although large organizations have more resources to address cybersecurity requirements, small organizations are expected to comply with the same requirements even though they may only have 1-100 employees. Companies with 100-200+ employees can also face challenges in meeting their IT needs, let alone addressing cybersecurity.
Board members may be unaware that they can be held liable for cybersecurity breaches, or for failure to address legal and regulatory cybersecurity requirements. CEOs may be unaware that in most cases, they are considered to be the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) of their organization, even though they may only have a few employees. An employee who already has a full-time job and does not have sufficient knowledge to address cybersecurity may be forced into the role of Compliance Officer (CO)—leaving both the employee and the company open to liability due to negligence. Internal IT staff may not be adept in cybersecurity and the need to balance functionality and security. Network/System Administrators are concerned with ensuring that everything is working properly and that end users have easy access to the tools they need. End-users may lack the awareness and training to identify phishing emails, wire transfers, and CEO fraud, amongst other attacks. All of the preceding problems may leave a small business vulnerable to cyberattacks and liable for not taking appropriate protective steps.
Cybersecurity is a critical business need and function, and unmanaged cybersecurity can expose organizations to incidents from which they may not be able to recover. Breaches can expose organizations to financial losses: legal, contractual, and regulatory liability; loss of reputation; loss of customers; and loss of trust. The management of cybersecurity and the establishment of a risk management program helps an organization prepare for a data breach and supports its survival.
Learn how to protect your organization before it is too late.
Thank you,
Marlon Bermudez
Marber Security LLC
www.MarberSecurity.com